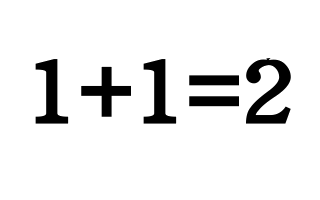The PostERP framework
ERP software quality determines the success or failure of an organization's digital transformation
- The core quality of ERP software cannot be significantly improved in the process of implementing ERP projects.
- The number of consultants can increase at any time. The consultants can be replaced with experts with higher academic qualifications and more experience at any time.
- The management strategies, quality assurance and supervision measures, communication skills and frequency, and user training hours and quality used in ERP implementation process can all be added, adjusted, improved, or even repeated at any time.
A large number of cases prove that once the core quality of ERP software is poor, the improvement and adjustment measures 2. and 3. will be completely ineffective. Those ERP projects that use inferior ERP software have only three outcomes:
- It ended in direct failure and the software was discarded.
- Organizations reluctantly use 1 or 2 modules such as accounting and sales, but stakeholders still declare "success" to the outside world.
- Organizations continue to add personnel and hardware tyring to keep their projects afloat.
ERP quality will ultimately be reflected on the profit and loss statements of its corporate clients. ERP quality has a profound impact on its users' operating costs, growth momentum, corporate image, R&D and customer service, and the morale of personnel in various departments such as public relations.
Characteristics of PostERP
- Universal
- ERP application system development and operation framework
- High flexibility
- Simple, lightweight and low system development threshold
- Database driven
- Uses PostgreSQL
- Pure browser UI
- High-speed backend software
- Client software is lightweight
- Easy to operate
- Internationalization
- Capable of reporting
- Elegant accounting module
- File attachments
- Provides simple and efficient API
- With security protection mechanism
- Provides both cloud ERP services and buyout ERP products
1. Universal

IT personnel develop ERP application systems for unlimited industries on the PostERP framework
- The PostERP framework is suitable for use by enterprises in various industries, including governments, schools, non-profit institutions, and countless other industries.
- PostERP is suitable for enterprises of all sizes, from one-person companies to multinational groups.
1. Other programmed software packages can only be used in specific industries:
- An ERP may be used by factories with simple business nature, but it is not suitable for car rental companies, life insurance companies, chain retailers, natural gas companies, hospitals, banks, post offices, electric power companies, wafer factories, and oil companies, tire factories, water plants, freight forwarders, schools... and other non-manufacturing enterprises and government departments.
- An ERP may be used by manufacturing factories with low requirements, but pharmaceutical factories, shoe factories, and clothing factories that strictly require "batch number" control will be miserable if they buy it.
- The architecture of an ERP is not suitable for developing human resources systems.
- An ERP "for Shoe Factory" cannot be used in machine tool factories.
- An ERP is suitable for enterprise use, not suitable for government departments; or vice versa.
Once a set of package software that is only suitable for specific industries is forced onto corporate users in different industries, its scope of use may be reduced to accounting modules by the user companies, or even be turned into data storage center.
2. Other brands of ERP can only be applied to certain scale enterprises:
- The "Large Edition" ERP is suitable for large enterprises.
- Because it is too complex, it cannot be used by small businesses and one-person companies.
- The "Small Edition" ERP is suitable for small businesses and one-person companies.
- Because an ERP is too vanilla and rigid, if it is used by large enterprises, it will lack too many functions and does not allow expansion.
2. ERP application system development and operation framework
There are many strategies for developing ERP application systems.
1. The shotgun strategy of other ERP brands
This strategy is also called the panacea or snakeoil strategy. Its ultimate use is technicians doing their best to pre-make programs or modules one by one on the basis of experience or guessing all the software functions that different companies may need, waiting for corporate customers to select or bundle them all for sale.
The ERP pre-fabricated according to this strategy are bulky, complex and difficult to use:
- They have many screens, many programs ("transactions"), many switches, and many parameters.
- They have many hidden mechanisms, many linking mechanisms, and the mechanisms constrain or exclude each other.
- Manuals and online instructions are difficult to cover clearly, manuals are wrong or outdated, and inconsistent with the software.
These software have the following flaws:
- Pre-made products fail to meet the "special" or marginal needs of some companies.
- Because of the complexity, there may not be the kind of consultant who fully understands all or even a single module of the ERP. As a result, companies using such ERP are "urgently seeking consultants" all year round.
- Because these ERP architecture have major inherent flaws, software vendors themselves and partner consultants are unable to develop commercial application software according to the planned schedule and deliver it to enterprise users in real time.
- Because these ERP software are difficult to use, the process of training users is arduous, and users strongly resist to the project, resulting in difficulties in going online.
- Because these ERP software are bulky and rigid, it is difficult for IT staff to expand or modify ERP applications. As a result, the number of people in the IT department remains high, resulting in a heavy burden of personnel expenses for enterprise users.
- The back-end ERP software do not run fast, forcing enterprise users to purchase expensive hardware and set up huge infrastructure hardware and IT personnel.
2. The program generator strategy that has long since disappeared
The concept of "program generator" already appeared during the M$ DOS era. At the end of 2023, some people began to advocate using artificial intelligence (AI) to generate software.
What commercial software is generated using program generators?
- Can it be used to process business information from all walks of life?
- Can it replace existing ERP software?
- Is its execution speed higher than that of traditional hand-built software today?
- Can manual intervention be used to debug, enhance, and expand the software?
Suppose we now need a personnel salary module as shown below. Is there a program generator or AI robot that can automatically design it that handles the following situations?
- Three shifts: 07:00 ~ 15:00, 15:00 ~ 23:00, 23:00 ~ 07:00
- The night shift has snacks.
- If you are late for less than 30 minutes, your salary will be deducted by NT$500 for each late.
- Those who have made two outstanding contributions will be awarded three days’ salary as a bonus.
- Those who are 1 to 4 hours late must take half a day off.
- One day of wages will be deducted for absenteeism.
- Provide a monthly bonus of TWD 1,000 for perfect attendance.
- One warning will result in one day's salary deduction. One major demerit will result in 3 days of salary deduction.
- Except for those at manager level or above, all employees must swipe their on and off work cards.
- Factories have ranks – salary scales.
- Accommodation is provided for foreign workers.
- Provide discounted meals to on-site personnel.
- Implement labor insurance, health insurance, and salary income deduction mechanisms.
3. The building block strategy with a loud slogan that has now disappeared
"CORBA appeared a long time ago. I don’t know when terms such as "SOA" and "micro service" appeared to compete with it. I have never heard of anyone using this kind of thing to make a usable ERP.
4. PostERP framework strategy
This article from now on refers specifically to this PostERP application system development and operation framework.
3. High elasticity
Highly flexible ERP framework
The prerequisite for ERP to be universal is high flexibility. Those pre-made or even hard-coded software packages, no matter how many modules, how many switches, how many industrial samples, how many best configuration solutions, or millions of pre-made programs, they all belong to the shotgun ilk. These inflexible, complex, difficult to understand, difficult to use, and rigid systems cannot be used in "special" enterprises and government departments.
A concept must be clarified here. "Special" is actually a misnomer. Just because an ERP is not applicable to non-manufacturing industries, we should not refer to other industries as "special".
How should we structure ERP to comply with the principle of high flexibility?
"You want high flexibility? Programming languages have the highest flexibility! Just sell COBOL's sister ABAP, 4GL, Java, Python, C, PHP, ASP languages, and even assembly languages to customers, and ask their MIS personnel to develop their business application software in these computer languages!"
Although programming languages have the highest flexibility, this strategy is not advisable because it has a major disadvantage - lowest productivity.
In order to achieve both high flexibility and high productivity, MIS personnel should use < span class="productname">PostERP, the ERP application system development and operation framework.
4. Simple, lightweight and low system development threshold
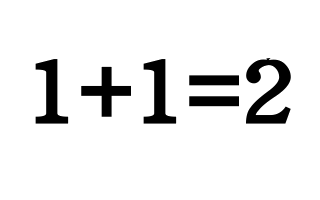
Simplicity and lightness equal high quality
ERP application systems should strive to be simple rather than complex, lightweight rather than bulky.
Only simple ERP will have high flexibility .
- This kind of ERP application system is easy to use.
- Users are willing to accept an ERP application system they can quickly be familiar with. Otherwise, they tend to resist the ERP software that is complex, difficult to use, and prone to misoperation.
- This kind of ERP application system saves enterprise customers' hardware investment.
- It can run at high speed on general-standard hardware and respond to users instantly. Otherwise, a complex piece of software is like a dinosaur: it crawls slowly on top of high-end hardware.
- This kind of ERP application system reduces the IT labor cost and time for enterprise customers.
- Because the ERP is easy to maintain, modify, expand, and run in multiple environments, IT staff, system integrators, and consultants are highly productive. Otherwise, a complex software does not obey the instructions of MIS personnel, refuses to be tamed and is unable to adjust, and the MIS staff hardly understand it, which leads to low morale among all participants and repeated delays in project progress.
- PostERPSimple
- The entire PostERP system consists of only a few components. It is not the kind of complex software that is stacked on top of each other and is intricately connected. It is not the kind of system whose source code is millions of lines and the installation file is hundreds of MB that organizational IT personnel and the software vendor's own engineers cannot fully understand it in their lifetime.
- PostERPLightweight
- The source code of the PostERP application system is very small. For example: the size of an uncompressed manufacturing ERP application system is less than 300 KB and can be easily maintained by any information personnel.
- PostERP's technical threshold for developing application systems is very low.
- Anyone with PostgreSQL technology and basic accounting knowledge can develop ERP application systems on the PostERP framework. Because the PostERP framework has Low Code Framework characteristics, so information personnel can easily extend and maintain ERP application systems, and Citizen Developer becomes possible. Enterprises can consider inviting accountants and actuarial staffs to develop ad hoc ERP applications for themselves.
5. Database driven
IT staff can complete the design of the following three CRUD screens through simple definitions on the PostERP framework without writing any programs. Therefore, the PostERP framework is "database-driven".
Take the company’s sales business as an example. Its main businesses include:
- Sales Order
- Shipping
- Sales returns
"Database driven" is not a new buzzword. Database-driven PostERP framework empowers IT staff with maximum productivity, allowing technical staff to work on it at lightning speed developing various ERP application systems and completed ERP projects in a short period of time.
6. Using PostgreSQL

PostERP uses PostgreSQL
PostERP uses PostgreSQL database management system (Data Base Management System, DBMS).
- PostgreSQL is the world's most advanced open source DBMS, and its performance meets the requirements of a high-quality ERP framework.
- Enterprise customers are exempt from purchasing DBMS licensing and maintenance fees.
- PostgreSQL provides excellent quality manuals second to none.
- Technicians have easy access to high-quality technical services.
7. Pure browser UI
You can use any large-screen desktop computer, laptop, or tablet, open any mainstream new browser, enter the PostERP website address, and operate PostERP directly without installing any plugins.
8. High-speed back-end software
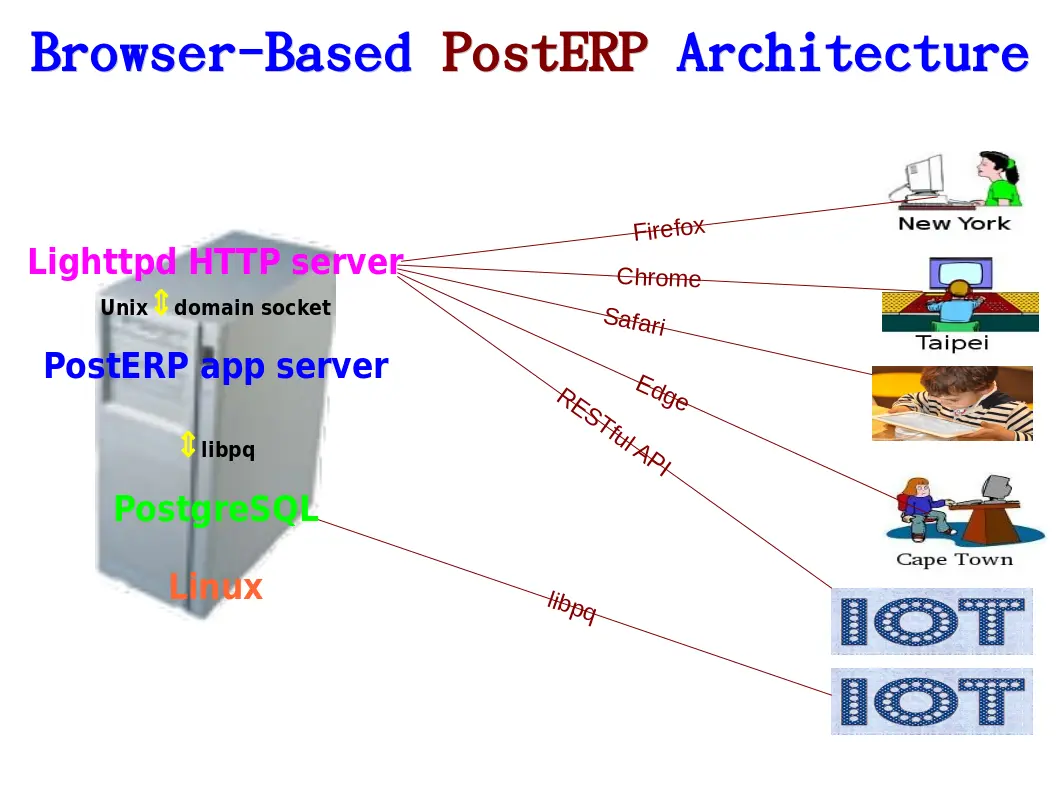
An ERP with a simple structure can run at high speed
As the number of customers increases and the complexity of business logic grows, the lengthy response time of ERP server software becomes a point of criticism. Slow-running ERP server software wastes users' valuable time and reduces their work efficiency.
Because some ERP server software runs slowly, its manufacturers instead require their customers to purchase high-end hosts for their server software to run on, using their software flaws to drive up the selling price of their products.
This architecture is flawed because the bottleneck in the overall ERP system's operating speed lies in the software, not the hardware. Therefore, ERP enterprise users invest money in hardware, which does not significantly improve the overall operating efficiency of the system.
Because they process business logic in server software, these ERP systems are extremely slow, and they consume a large amount of network bandwidth between the server software and the DBMS. These ERP systems operate as follows:
- After the client program receives a request to execute MRP, the server software first reads data from the DBMS. The server software then scans the read data. With each scan, the server software reads more data records from the DBMS. This process continues iteratively, chaining data reads from the DBMS. This data processing strategy is inherently inefficient: the server software reads as much data as possible from the DBMS, consuming significant amounts of RAM and CPU.
- If the server software and DBMS are not on the same host machine, then enterprise users must invest in high-end network equipment to enable high-speed data transfer between the server software and the DBMS.
- Data processing in the server software is far less efficient than direct processing by the DBMS. The reason is simple – all DBMSs, especially PostgreSQL, optimize their data processing. The DBMS knows how, when, and whether to read which data to minimize CPU, RAM, and hard drive costs. However, server software has little control over these resources.
Complicating simple problems by inventing a bunch of unnecessary and magical mechanisms is futile; the return on investment for organizing users may actually be negative.
The PostERP server software is lightweight and simple. It acts as an intermediary between the browser and PostgreSQL. It runs with unparalleled lightning speed:
- MRP calculations, accounting settlements, payroll calculations, and other business logic are all executed within PostgreSQL functions and procedures.
- Upon receiving a request from a client program, the PostERP server software verifies the requester's identity and permissions.
- The ERP server software searches the cache for the required result. If found, it immediately responds to the client software.
- If the ERP server software does not find the answer in the cache, it forwards the request to PostgreSQL. After receiving the answer from the DBMS, the ERP server software immediately replies to the client program.
PostERP server software plays this simple role, nothing more, nothing less:
- PostERP server software does almost no computational work.
- Changing the business logic does not require changing the PostERP server software code, nor does it require a restart.
- The PostERP system is simple, easy to maintain, and has virtually no bugs.
- It can run at lightning speed on a host with 1 GB of RAM, instantly responding to a massive number of client program requests.
The PostERP backend system with a featherweight physique is a strongman
9. Customer software is lightweight

The front-end of the PostERP framework is a 1 MB client software running in a browser
ERP, where the client installation software often requires four CDs, is already outdated.
Customer software for PostERP framework:
- Browser version: 1 MB software that runs in the browser
- Desktop version: A single execution file with a size of only 1.7 MB. Users can directly double-click to execute it on Windows. Users do not need to install it, and information personnel do not need to distribute or deploy customer software.
10. Easy to operate
PostERP's client software is easy to operate, reduces training work, shortens the system launch period, improves users' work efficiency, and reduces users' rejection of PostERP.
- Reduce the number of CRUD screens and menus.
- Easy to use. Users can complete their daily work by operating PostERP on a few screens. Avoid forcing users to open multiple CRUD screens, switch back and forth, compare, search for data between screens, and operate CRUD.
- The manual has few pages.
- Users can actually operate the software in just a few minutes.
- Provides extensive online help in a variety of languages.
- Screen description, field description, report purpose description, report parameter description, business logic processor description, business logic processor parameter description. Users no longer have to dig through outdated manuals that have been in disrepair.
- Every screen has the same appearance and layout.
- It takes time to adapt to the ERP operation screen. We should avoid designing this kind of system: different CRUD screens have randomly arranged fields, and different mechanisms such as buttons and pop-up windows.
- Easily search for information.
- For example: Users can search records for each field on the CRUD screen.
- All records displayed on the screen are allowed to be downloaded by users.
- Provide menus to users.
- Avoid forcing users to recite the program code ("transaction").
11. Internationalization
PostERP is suitable for multinational enterprises
PostERP supports multi-language, multi-time zone:
- Multilingual
- One program supports all languages. It's not like writing 4 versions of a program with the same functions: version 1 supports Traditional Chinese, version 2 supports Simplified Chinese, version 3 supports English, and version 4 supports Vietnamese.
- The client software allows users to switch languages online without having to log out and then log in again.
- After IT staff designs a report, users print the report in various language series.
- Multiple time zones: Taking [shipping date] as an example, ERP users in London see 2019–12– 25 11:09:03.356505+00, ERP users in Taipei saw 2019–12–25 19:09:03.356505+08.
12. PostERP has reporting capabilities
- PostERP has complete reporting capabilities
- It allows IT personnel to design various reports to meet the diverse and complex needs of users.
- PostERP provides IT staff with unrivaled report production productivity
- IT personnel create various complex reports required by users on PostERP. Each report is produced in minutes, not days.
- PostERP integrats reporting functionalities
- After the IT staff completes designing a report, the user immediately selects the report from the menu and starts to print it. IT staff does not need to distribute reports to each user. PostERP is different from this kind of ERP: the reporting function is a plug-in component separated from ERP.
- IT personnel do not need to use third-party tools to design reports and end users produce reports. PostERP reports require zero deployment - After IT staff designs a report, end users on the other side of the world immediately select the report from the menu and print it. IT staff does not have to distribute report templates to users. PostERP's reporting functions are self-sufficient and do not require independent third-party reporting tools.
crosstab report
13. Elegant accounting module
- PostERP's accounting module is not a low-quality accounting module where accountants have to spend 45 days to complete the accounting closeout.
- PostERP's accounting module is seamlessly integrated with each business module to generate entries in a timely manner, keeping them up-to-date. Users can obtain the latest financial information and the latest business performance information at any time, without having to wait until the accounting closes at the beginning of the next month.

Seamless integration of accounting modules
- Accountants using PostERP do not need to quarterly, semi-annually, or annually close accounts. Accountants only need to do a very small amount of daily jobs and monthly close accounts.
Accountants using the Manufacturing Edition and Distribution Edition of PostERP do not need to run the "cost calculation" batch program. The system displays the latest cost information at any time.
PostERP guarantees that there will be no negative amounts, uneven debit and credit, negative quantities, etc.
PostERP absolutely prevents inconsistent data between modules. For example: item A,
- Displayed on the sales screen or report: 10 units sold, cost of goods sold is $2 /unit.
- Displayed on the inventory or cost screen: 11 units sold, cost of goods sold is 3 $/unit.
14. Attached file mechanism
To move closer to the paperless goal, PostERP provides a mechanism for users to upload files, attach them to the data record, and allow for future downloading. For example:
- The R&D personnel upload the processing description drawings and attach them under item A for downloading and reference at shop floor.
- Patent office personnel upload incoming and outgoing letters with correspondants and attach them under the project application progress date 2020–1–1 for future reference.
15. Provide simple and efficient API
- IT staff do not need to write programs, PostERP automatically provides RESTful API for peripheral devices such as IoT, WMS and MES to call and directly perform CRUD operations on the target database table simply, efficiently and safely.
- Peripheral systems can call PostgreSQL's libpq to exchange data with PostERP at high speed.
16. With security protection mechanism

PostERP has high security
17. PostERP provides both cloud ERP leasing services and locally deployed ERP products.

PostERP has a cloud ERP services for you to rent; and ERP software products for large organizations to purchase and deploy in your own computer room.
- Medium, small, and micro enterprises rent cloud PostERP services to work from home, travel abroad, and operate globally on the go.
- National defense departments and large multinational companies purchase the PostERP framework, on which IT staff can tailor-make ERP application systems that 100% meet business needs.